To see bees in nature is a simple matter. However, in addition to the usual honey plants, in the world there are several thousand varieties of these insects.
Description and Features
The bee belongs to the superfamily of stinging insects Apoidea. It is closest to wasps and ants. Worldwide, there are approximately 21,000 species and 520 genera of bees.

Insects feed on pollen and nectar. At the same time, pollen serves as a source of useful substances for them (in particular protein), and nectar - energy. Some species have the highest social organization.
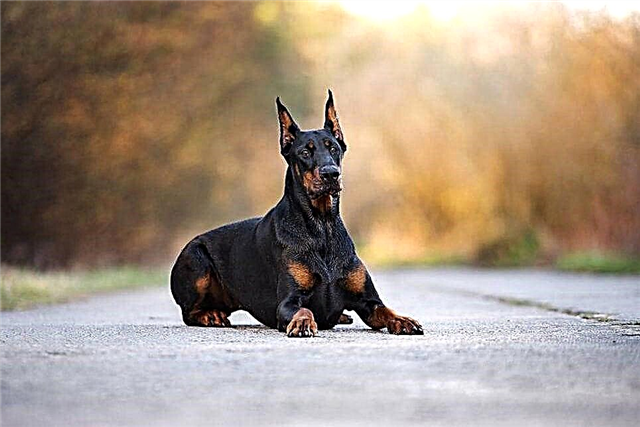
Bees can have a different appearance depending on a particular species. But on average, they differ in size about 3 centimeters and a striped color, in which yellow-orange and black colors alternate. The body is completely covered with hairs, which serve as protection and perform the function of the organs of touch.
A distinctive feature of the bee is the presence of a proboscis to suck out nectar and a sense of taste. And the antennae are responsible for the sense of smell, recognize heat / cold / humidity. Some parts of the body and legs act as hearing organs.
The structure of what a bee looks like

Bee belongs to the category of arthropod animals. Her body consists of three main parts:
- the head;
- chest part;
- abdomen.
Also a distinctive feature of insects is the outer skeleton, which is presented in the form of a protective hard shell. Muscles and internal organs are attached to it.
The head of the bee is protected by a layer of chitin. In addition to the antennae, she has an upper lip and an oral apparatus with well-developed muscles. This allows insects to carry small objects and bite through any natural materials.
The thoracic part consists of several departments. Here are the muscles with which the bee controls the wings. She also has three pairs of legs. The hind legs are most covered with hairs on which pollen is carried. Front legs are used by insects for personal hygiene.
Interesting fact: Bees can reach speeds of up to 60 km / h, while doing about 400 wing flaps per second. If the insect does not fly “light”, but with some kind of cargo, then its maximum speed is up to 20 km / h. The largest weight of tolerated severity is up to 75 mg.
Almost all internal organs are concentrated in the abdomen. It consists of several segments that are connected by an elastic film. On the abdomen are special glands (4 pairs) that secrete wax.
The most important organ of the bee is the sting. She uses it for defense, but in case of loss, the life span of the insect is reduced to a couple of hours. The fact is that the sting is very sharp and has notches, unlike a wasp. Attacking the enemy, the bee tries to pull it out and thereby damages its organs.

Habitat - where do bees live?
Bees are considered fairly common insects. They do not inhabit only those territories where there are no flowering plants. Such areas include hot deserts and cold tundra. In other natural areas, bees can be found everywhere.

Lifestyle & Habitat
Favorite habitats of wild bees are mountain crevices, earthen burrows, hollows of old trees. Bees choose sites that are located near water bodies, and are also reliably protected from difficult weather conditions, wind.

In a mild climate, nests settle high on trees. Having chosen a suitable place for housing, they begin to build cells from hexagonal cells. Each cell has thin walls. Honeycombs are mounted vertically and have an elongated shape. Special frames adapt for domestic bees, and wild insects build their own honeycombs.
Before the onset of cold weather, the main task of bees is to stock up on provisions and insulate housing.They do this with propolis, which smears all the cracks. Then the insects move to the lower part of the nest, where they stick together, periodically changing places.

Interesting fact: comfortable temperature for bees - 25-36 ℃. In winter, inside the nest they maintain a temperature of about 13 ℃.
In general, wild bees differ from domestic ones only in some features of their behavior and character. For example, they are more aggressive because they have more natural enemies and are forced to defend their stocks. They are also more resilient, more resistant to colds and diseases.
Bee organization
The bee organization system deserves special attention because they have their own hierarchy. There are several types of bees, depending on their lifestyle:
- public and semi-public;
- single.
Public
The most developed in terms of coexistence are social insects. These include melliferous, stingless bees and bumblebees. A labor insect colony is called semi-public. In a social group, bees have certain responsibilities, but at the same time they represent the common offspring of the mother.
Highly-public bee colony is singled out separately - its members have different body structures and certain responsibilities. They complement each other. The highly social swarm is represented by a single queen, working bees, and drones.
Uterus there is always only one in a group; it stands out significantly in size compared to the others. Its main function is procreation. The uterus is considered the main individual in the colony, so the rest of the bees protect it and provide food.

Working bees - females, which form the basis of the group in numbers. They can most often be seen in nature. One nest numbers about 80,000 individuals. Representatives of the working group are looking for suitable plants, they extract nectar, make honey.

Another members of the swarm - male drones. Their main task is to continue offspring. Drones do not produce pollen and do not make honey. They are larger than working bees and need more food. When the drone ceases to be useful for the colony, it is simply expelled. In general, they are not able to winter the cold.

Single
There are many more single species of bees. They do not have a system for dividing into working individuals, etc. New offspring appear due to one type of females, which also get food. Often they do not produce additional substances like wax or honey.
Vision
The bee has two types of eyes: three simple at the top of the head and two complex at the sides.

Complex eyes are called faceted. They have a convex oblong shape. If you increase this eye several times, you can notice a huge number of hexagons on the surface. Worker bees have about 6,000.

Each such cell is a peephole formed from visual cells. Due to the specific structure of the eyes, the bee sees the image less clearly - it resembles a picture divided into separate points. It’s easier for her to watch moving images than static ones.

Simple eyes have a similar structure, but they are too poorly developed to perceive the image. Their function has not been reliably studied, but most likely, with the help of simple eyes, insects distinguish between light and darkness.
How long does a bee live?
Bees can have different lifespan depending on the function in the colony, as well as the time of birth.
The queen bees live the longest - about 5-6 years. Since the uterus is fully provided by working bees and protected from dangers, it must regularly give new offspring.
In second place are working bees. Individuals born in the warm season usually live very little - no more than a month. It’s all to blame for the hard daily work in high season.
Sometimes bees are born in autumn. In this case, their lifespan reaches about six months.Each such insect must overwinter and fulfill its direct duty in the spring.
Drones live the least. Having been born, they fulfill their mission and soon perish. If drones remain in the hive before the onset of cold weather, they are driven out by the working caste and also die, left without a house or food.

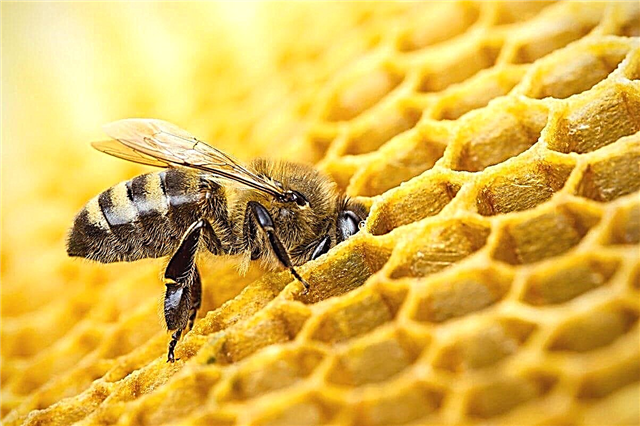
How do bees make honey?
To produce honey, bees need nectar - a very sweet juice secreted by flowering plants. The insect collects nectar with a proboscis, after which it enters a special organ - a honey goiter.

In the saliva of the bee there are enzymes that enter the goiter along with nectar and break down the carbohydrates contained in the juice. Each enzyme performs its function:
- Invertase - accelerates the breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose.
- Glucose oxidase - breaks down glucose into gluconic acid (the taste of honey depends on it) and hydrogen peroxide. It is noteworthy that peroxide first purifies honey from microorganisms, and then breaks up.
- Diastase - breaks down starch into simpler carbohydrates.

Returning to the honeycombs, the bee begins to fill them with collected nectar. Here in the hierarchy appears a subspecies of worker bees - a kind of receiver. They are engaged in the production of honey further, and the collecting bees again set off for new nectar.
Insects perform the same procedure about 200 times. They allocate a little nectar to the proboscis so that moisture evaporates from it, and then again they are sent to the goiter. Thus, the substance is fermented until it turns into honey.

Filling the cells, the bees continue to pour honey from place to place, and also air the honeycomb with a wave of wings. All these actions are aimed at removing all moisture. Cells with finished honey are sealed with wax.
Interesting fact: To make 100 g of honey, bees need to collect nectar from about one million flowers.
What do bees eat?
In the warm season, bees feed on pollen and nectar from flowering plants. From here they also take water, and sometimes collect dew. Pollen is the main "building" material for the body - protein. It helps strengthen muscles and the endocrine system.

Nectar helps a bee to replenish energy reserves, in other words, it is a carbohydrate. In winter, insects feed on honey, which they produced all season. Honey also provides energy.
Enemies of the bees
Bees have a lot of natural enemies. Among them there are both insects and birds. Among insects, these are predators: mantises, spiders, bee-eaters (wasp genus). Regularly attack bee nests of birds, which are representatives of the families of swifts, flycatchers, shrikes, etc. They are also food for lizards.

How are bees different from wasps?
Despite the apparent similarity, there are many differences between bees and wasps. They can be found in appearance, lifestyle and behavior.
Compared to the round body of a bee, the wasp has a more elongated and longer shape. It has a minimum of hairs (on the abdomen they are completely absent). The chest area is tightened. Color - yellow-black striped, but much brighter and more noticeable than that of bees.
For the bee, hard work for the good of the colony, the hive is the meaning of life. They collect nectar, pollinate plants, produce honey, make honeycombs from the produced wax.
The structure of the wasp organism is not designed to produce any valuable substances. The construction of nests is carried out by them from various materials, for example, old wood. The diet of wasps is more diverse, it includes nectar, fruits, as well as other small insects.

A bee attacks an adversary only if it senses a threat or attacks in response. Insects in one colony constantly take care of the uterus.
The wasps have a more aggressive, predatory character. They can sting at any time. The wasp sting has a different structure, so it is able to attack an unlimited number of times without harming itself.A wasp can also bite using the jaw apparatus.
Among wasps there are also public and solitary species. However, in an aspen society, the uterus provides itself independently, and also actively participates in the construction of the nest.
In addition, bees occupy a clear place in the classification and have a scientific definition. Wasps can be called any representatives of stinging stalk-bellied insects that do not belong to ants or bees.
Bee species
The Apoidea superfamily is represented by several families: real bees, andrenides, haliktids, and others. In total, they form 520 genera and thousands of species diversity.
All bees can be divided into 2 categories: wild and domestic. It is not difficult to distinguish a wild bee: it is smaller in size, differs even more dull in color, the hairs are thicker and longer, and there is a protective shell on the chest part.

The greatest species diversity is characterized by a family of real bees - about 5700 species. Among them, it is worth highlighting honey plants and bumblebees.
Honey bees are actively used by humans. There are many breeds that can be successfully bred. If, a long time ago, bee nests were simply plundered with the aim of obtaining honey, now special wooden hives are being built for them. In addition, domesticated insects receive the necessary care, shelter, top dressing, etc.
Just honey plants and characterized by the highest level of organization, a clear distribution of responsibilities in the colony. One category, for example, working bees cannot live without others - drones and uterus, and vice versa.

Bumblebees also represent one of the interesting genera. There are about 300 different species that have much in common with honey plants. Bumblebees of a sufficiently large size, rounded in shape, can have different colors (mostly striped). They are more resistant to cold, therefore they are able to go to collect nectar before other species.

Some bees, for example, megahilids, stand out against the background of more familiar species. They are much larger, do not produce honey, live in numerous colonies and are characterized by aggressive behavior. The wingspan of such bees reaches 6 cm.
Parasitic bees
There are whole subfamilies among bees kleptoparasites - insects that appropriate other people's nests, food. In other words, they live off the labor of other bees. They are called cuckoo bees because of the similarity of behavior with the birds of the same name.

In such species, the body is not sufficiently developed to collect pollen and nectar. They also do not equip nests. Instead, insects toss their eggs into other people's homes. When a kleptoparasite larva appears, it can destroy other larvae, all food. Sometimes such bees destroy the uterus of the colony, and they themselves settle in the nest.
Bee breeding
Bees breed by laying their eggs with the uterus. If the drone participated in fertilization, working individuals will appear from the eggs; if not, drones.
Development takes place according to the following chain: egg - larva - pre-pupa - pupa - bee. In order to grow a young uterus, it is necessary to take special care of the larva and feed it with special milk longer than the rest. In this case, the reproductive organs develop better.

Over time, the colony of bees may become too large. In this case, a family division or swarming occurs. In this case, the young uterus remains in the same place with part of the family, and the old one flies away with other bees.
Benefit
Bees are one of the most beneficial insects. Their value is as follows:
- production of honey, wax;
- pollination of plants and increase yield;
- vital products of bees (poison, bee bread, royal jelly, propolis) are widely used in medicine.

Breeding
Bee breeding is considered an interesting, useful and profitable occupation, which is also actively welcomed in many countries.The fact is that in nature there is a constant decrease in the number of these insects, which can adversely affect agriculture.

For a novice beekeeper, breeding begins with arranging an apiary in the right place, acquiring a sufficient number of beehives, and also buying several bee families. To engage in this business on a large scale, you need to have about 50 families.
There is a huge variety of honey species of bees, and new ones periodically appear due to the selection work of experienced beekeepers. In general, it is worth noting that this activity is not simple, since many factors, both depending on the beekeeper and random, can adversely affect the quality and quantity of honey.

Interesting fact: Experienced beekeepers use smoke to soothe insects. This method allows you to quickly inspect the hive. Sensing smoke, the bees consider it a sign of fire and rush to save honey. At the same time, they fill the abdomen so much that they cannot sting for some time.
What to do if a bee has bitten?
When a bee stings, the most important thing is to get rid of the sting as soon as possible, which in most cases remains at the site of the bite. The sting contains poison, and the longer it comes into contact with the body, the more poison will enter the body.
The poison causes pain, redness and swelling. It is important to remember that the body of each person can respond in its own way to a bee sting. If the insect has stung in a particularly sensitive area, for example, the area of the face or neck, while there is severe swelling, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Serious allergic reactions are possible.

If you do not suffer from allergies, then you can carefully remove the sting yourself, using tweezers or the tip of a knife. Then it is recommended to wash the bite site with soap and water, an antiseptic, apply ice to the swelling - this will help get rid of the swelling much faster.
The anti-inflammatory agent will not hurt either. It is also advisable to position the limb (if the bite fell on it) as high as possible. This ensures the outflow of blood and the decline of puffiness.